overview

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent challenges in social communication and interaction, as well as restrictive and repetitive behaviors. The symptoms can vary widely, ranging from mild to severe. Some individuals may struggle with nonverbal communication and avoiding eye contact, while others may engage in repetitive behaviors or have specific, intense interests.
Early diagnosis and intervention are critical, as they can significantly improve outcomes. Interventions often include therapies like Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy. The causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder are not fully understood but are believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Autism Spectrum Disorder is often associated with co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, sensory sensitivities, and gastrointestinal issues. The approach to managing autism typically involves a multidisciplinary team to address the various needs of the individual, ensuring that both the core symptoms and associated conditions are managed effectively
WITHIN USA
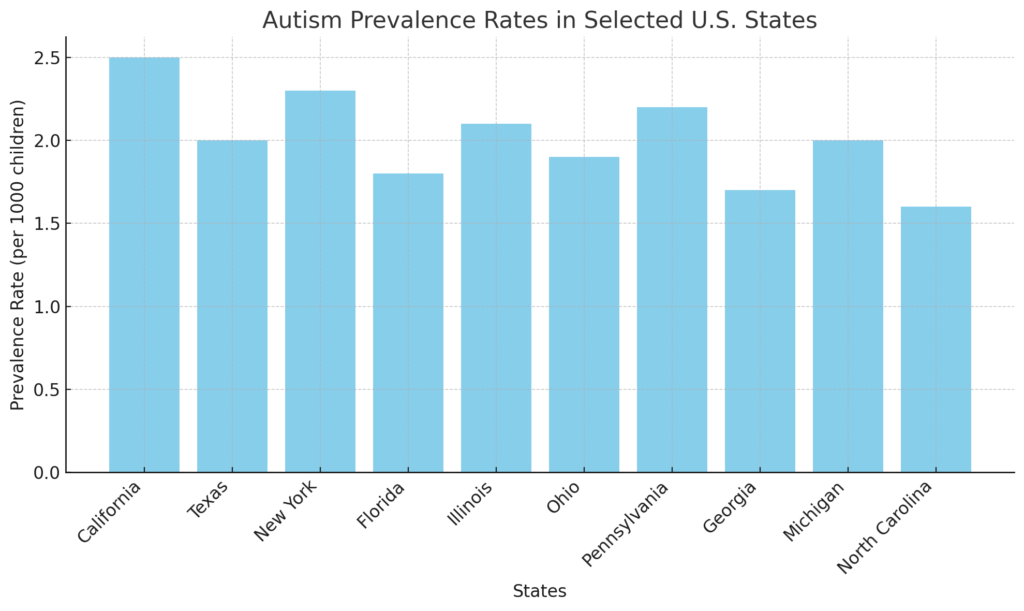
The graph displays autism prevalence rates across selected U.S. states, with values ranging from 1.6 to 2.5 per 1,000 children. California shows the highest prevalence at 2.5, followed by New York and Pennsylvania, both above 2.0. States like North Carolina and Georgia exhibit the lowest rates, below 2.0. The variation in prevalence across states may reflect differences in diagnostic practices, healthcare access, or demographic factors.
IN OTHER COUNTRIES
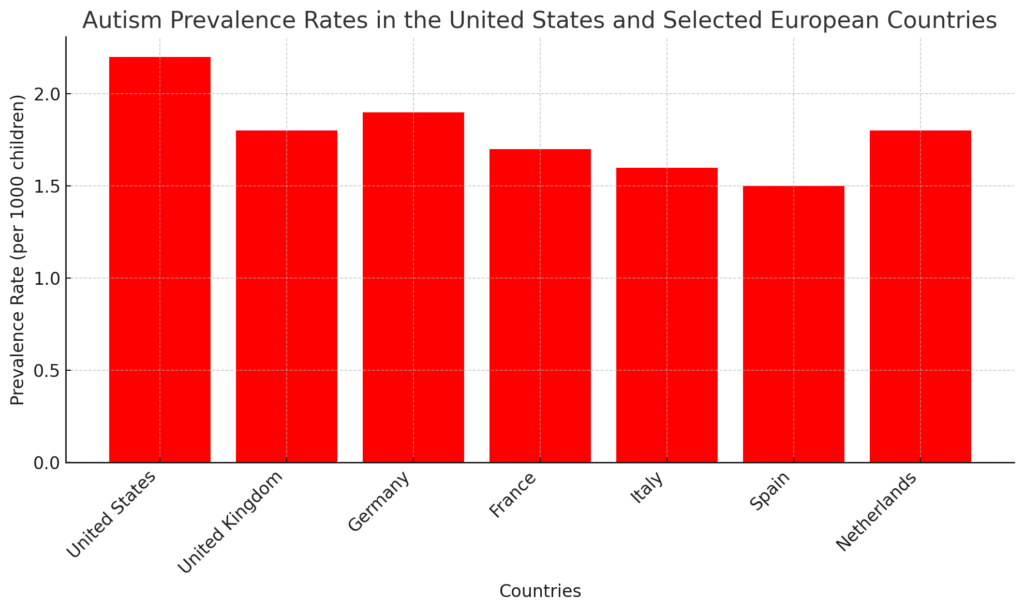
The graph compares Autism Spectrum Disorder prevalence rates between the United States and selected European countries, with rates ranging from 1.5 to 2.2 per 1,000 children. The United States has the highest prevalence at 2.2, followed by Germany and the United Kingdom, both around 1.8 to 1.9. Countries like Spain and Italy show lower prevalence rates, around 1.5 to 1.6. . The higher rate in the U.S. could indicate more widespread screening or reporting practices, while lower rates in Europe suggest possible underdiagnosis or varying healthcare approaches.
Autism Spectrum BY GENDER
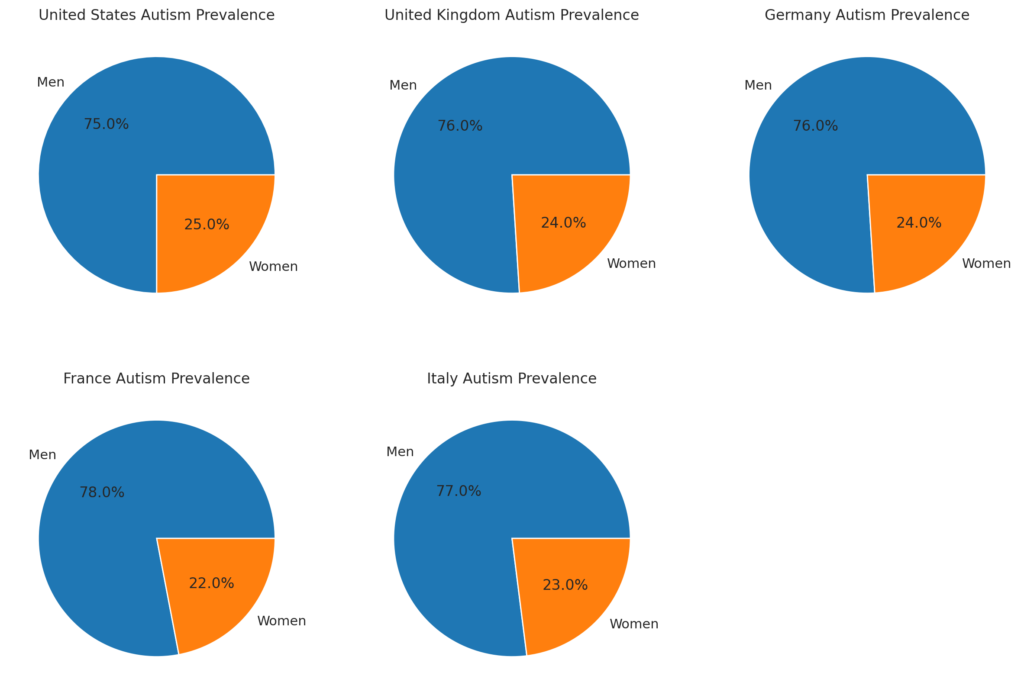
The pie charts illustrate the gender disparity in Autism Spectrum Disorder prevalence across five countries: the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Italy. In all countries, the prevalence is significantly higher among males, with percentages ranging from 75% to 78%, compared to 22% to 25% for females. This consistent pattern across different regions highlights the well-documented gender difference in autism diagnoses, where males are diagnosed at a much higher rate than females. The data suggests that while autism is a global concern, it disproportionately affects males, necessitating further research to understand the underlying causes and to tailor interventions accordingly
